
Accelerating the Transition to EVs through Climate Financing
The transportation sector is a significant contributor to global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. In 2021, it was responsible for almost 37% of all global emissions, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). This makes it one of the largest contributors to climate change and underscores the urgent need to transition towards more sustainable forms of transportation. Many countries around the world have already taken steps towards this transition, with policies and regulations aimed at encouraging the adoption of Electric Vehicles (EVs). These policies include incentives for consumers and businesses, such as tax credits, rebates, and subsidies, to purchase EVs. Additionally, some governments have set targets for the percentage of EVs in their national fleet or have implemented regulations to reduce the emissions from vehicles. Despite these efforts, the shift towards EVs has been slower than anticipated, and the transition still presents significant challenges for businesses, public and private sectors.
The high cost of EV technologies in comparison to traditional vehicles has been identified as a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of EVs. This challenge has resulted in many stakeholders (e.g., businesses, government, organizations, etc.) finding it difficult to justify the necessary investment to transition towards electric mobility. The high cost of EV technologies can be attributed to several factors, including expensive batteries, limited local manufacturing capabilities, and insufficient economies of scale. These challenges have resulted in governments continuing to invest in internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
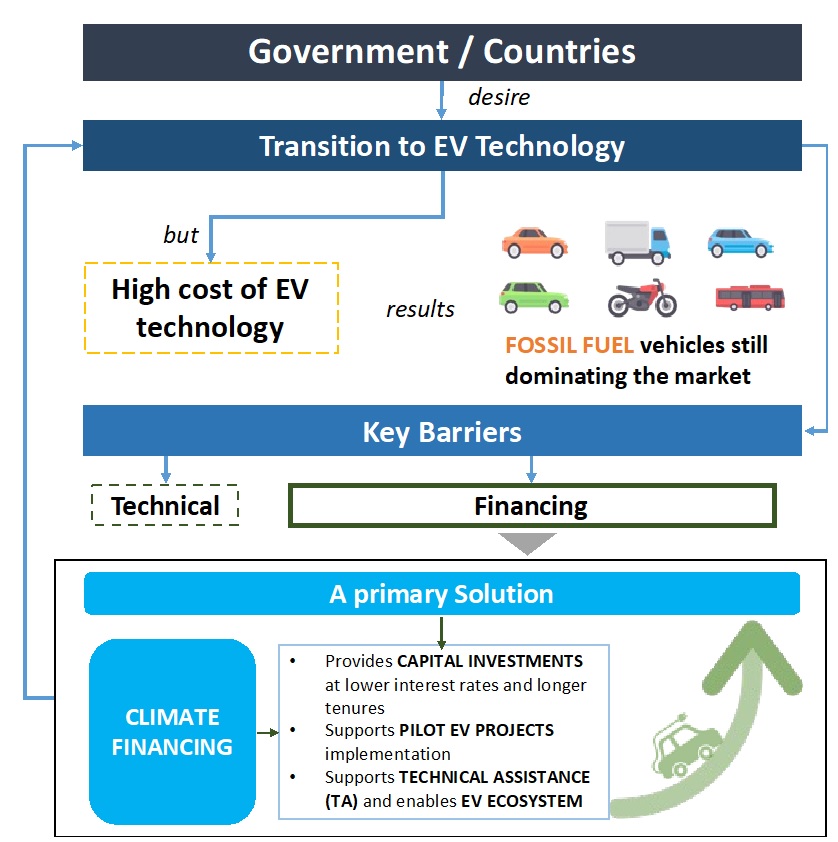
The transition to sustainable transportation solutions also faces significant financial barriers, including the limited availability of financing alternatives and restricted credit access. These challenges make it difficult for stakeholders to invest in EV solutions, thereby impeding the shift towards a low-carbon future. In addition to financial hurdles, other factors such as insufficient technical expertise, inadequate charging infrastructure, unsupportive regulatory frameworks, limited availability of spare parts, and others contribute to the already substantial barriers hindering investment in sustainable transportation technologies. Climate financing is expected to play a crucial role in promoting the uptake of EVs globally as it can help overcome the financing requirements associated with EVs by providing a range of financial instruments to address the challenges. By leveraging these financial tools, it can help reduce the upfront costs associated with EVs and address several market failures related to financing, including:
Mobilizing capital for sustainable transportation projects
The financial barriers faced by countries/governments in investing in sustainable transportation projects are significant and multifaceted. These barriers include limited access to capital markets, high levels of debt, and other economic challenges that hinder their ability to effectively address the challenges posed by climate change. In order to overcome these barriers, climate financing agencies provide a range of financial instruments such as grants, concessional loans, guarantees, and other innovative financing mechanisms to help countries access the capital needed to invest in these projects. The provision of financial support by climate financing agencies not only helps them access the capital they need to invest in sustainable transportation projects but also stimulates investments from the private sector and other relevant stakeholders. This collaboration increases the potential for success and facilitates the development of sustainable transportation infrastructure that reduces greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and enhances climate resilience.
Providing financing with concessional rates and extended repayment periods
The transition to sustainable transportation technologies presents significant financial challenges due to high upfront capital costs, technology and operational risks. Access to commercial loans with high-interest rates in many countries further exacerbates the viability of these projects. To address these challenges, the climate financing supported project/programme provides funding at concessional interest rates and extended repayment periods, making the projects more financially feasible and attractive.
Supporting EV pilots to scale-up sustainable transportation market
The climate financing aims to create a conducive environment for the development of a scalable sustainable transportation market by supporting the pilot implementation of EV technologies. This approach provides valuable insights and learnings on the technological, economic, and operational aspects of sustainable transportation solutions. The insights gained from pilot projects will facilitate the successful scaling up of these projects, ultimately contributing to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change by promoting sustainable practices and reducing carbon emissions.
Enhancing capacity building/training for stakeholders
The climate financing program provides resources for capacity building, knowledge sharing, and technical assistance to equip stakeholders such as investors, project developers, and policymakers with the necessary knowledge and skills for successful implementation of sustainable transportation projects. The aim is to bridge the information gap between stakeholders and ensure informed decision-making.
It is evident climate financing will continue to play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of EVs in the coming decades. As the world increasingly shifts towards sustainable transportation technologies to combat climate change, the need for financing to support the transition to EVs is becoming more pressing. While climate financing is already being directed towards the transport sector, the current levels of investment fall short of the estimated annual needs. The estimated cost for investment in sustainable transportation technologies, including EVs, is between $2-2.8 trillion by 2030. Key players in climate financing such as Green Climate Fund (GCF), Global Environment Facility (GEF), International Finance Corporation (IFC), European Investment Bank (EIB), and others, are providing funding for various activities related to electric mobility, such as the deployment of EV charging infrastructure, purchase of EVs, establishment of EV supply chains, and capacity building and training programs for stakeholders. Therefore, it is crucial to increase investment in climate financing to support the transition to EVs and other sustainable transportation technologies, in order to mitigate the impact of climate change.


